Latest Posters

Poster
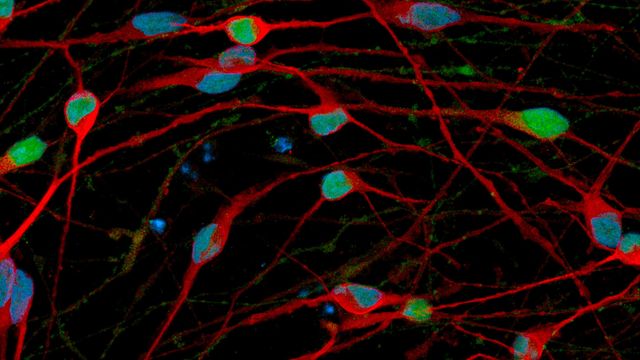
Discover a New Approach to Modeling Neurodegeneration
This poster demonstrates how a novel, precise and highly controlled iPSC reprogramming technology overcomes these limitations and enables the generation of mature cell types and isogenic models of neurodegenerative disease.

Poster
Optimized Human iPSC-Derived Sensory Neurons for Pain and Neuropathy Research
Many promising drugs which show efficacy in animal models have failed in the clinic due to interspecies variance in nociception mechanisms. Hence, consistent, scalable human in vitro models are required to accelerate potential therapeutics to the clinic.
Poster
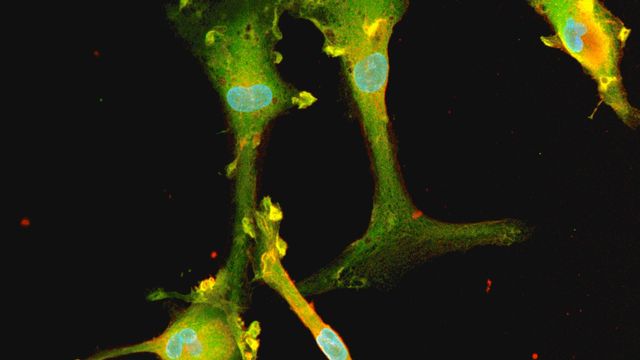
Generating Pure, Consistent GABAergic Neurons From hiPSCs
While animal models and primary cells remain valuable resources, neuronal drug development faces many challenges. Not least, the variability and inaccuracy of traditional model systems can result in the failure to translate data into successful clinical trials.
Poster
Functional, Reprogrammed Microglia To Study Neurodegeneration
Microglia play key roles in neurogenesis, synaptic remodeling, and are the first responders to infection in the brain. Hence, disease-relevant cell models are key to the success of neuroimmune and neurodegeneration research.
Poster
Modeling Neurodegeneration Using a Human Isogenic System
Patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) enable generation of in vitro models that can recapitulate human disease phenotypes. However, conventional human iPSC differentiation protocols are often lengthy, inconsistent and difficult to scale.
Poster
Modeling Neurodegeneration: A Next-Generation Approach To Study Huntington’s Disease
To overcome these challenges, researchers have developed a proprietary gene-expression targeting strategy that can rapidly reprogram hiPSCs into pure somatic cell types in a scalable manner. This approach was used to develop a Huntington’s disease (HD) model carrying a 50CAG expansion in the huntingtin (HTT) gene.
Poster
In Vitro Approaches To Risk Assess Chemical-Mediated Changes in Thyroid Function
The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis (HPT axis) is conserved across vertebrate evolution. Perturbation of thyroid hormone homeostasis (THH) can lead to adverse effects in thyroid function affecting growth, metabolism and cognitive function.

Poster
Spatially Resolved Transcriptomics of a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease
Download this poster to learn more about unbiased spatial gene expression,
application of spatial gene expression plus immunofluorescence validation and targeted analysis.
application of spatial gene expression plus immunofluorescence validation and targeted analysis.

Poster
Live-Cell Kinetic Analysis of Microglial Function and Morphology
Microglia are the resident immune cells of the central nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of homeostasis and the management of tissue response to inflammatory or pathological insults.
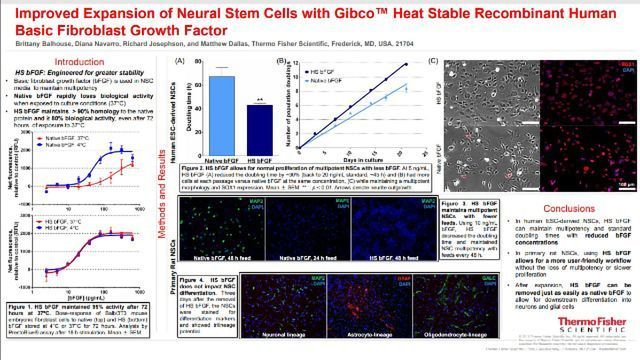
Poster
Improved Expansion of Neural Stem Cells with Gibco™ Heat Stable Recombinant Human Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is used in neural stem cell (NSC) media to maintain multipotency. Native bFGF rapidly loses biological activity when exposed to culture conditions (37°C), Heat Stable (HS) bFGF maintains > 90% homology to the native protein and ≥ 80% biological activity, even after 72 hours of exposure to 37°C.
Advertisement